Tracheal shave, a surgical procedure involving the removal of excess tracheal tissue to improve airway patency, is sometimes necessary for individuals with tracheal stenosis (narrowing of the trachea). However, it’s an invasive procedure carrying risks such as bleeding, infection, and potential vocal cord damage. This article explores alternative approaches to tracheal shave, focusing on less invasive techniques and therapies aimed at achieving similar outcomes with reduced complications.
Table of Contents
Understanding Tracheal Shave Procedures
Tracheal shave is typically performed using a bronchoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source. The surgeon inserts the bronchoscope into the trachea and uses specialized instruments to carefully remove the excess tissue causing the stenosis. The procedure is often used to treat benign tracheal stenosis resulting from conditions like intubation injuries, infections, or tumors. The success rate of tracheal shave varies depending on the severity of the stenosis and the individual’s overall health.
The procedure itself is relatively short, but recovery time can vary. Patients may experience some discomfort, coughing, and throat irritation following the procedure. Hospital stays are usually short, but close monitoring is crucial to detect and address any potential complications. While effective in many cases, tracheal shave carries inherent risks, including bleeding, infection, perforation of the trachea, and, critically, potential damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve, leading to vocal cord paralysis and voice changes.
Potential complications associated with tracheal shave necessitate careful patient selection. The procedure is generally reserved for cases where less invasive options have failed or are deemed unsuitable. Pre-operative assessments, including thorough imaging and respiratory function tests, are crucial to determine the suitability of tracheal shave and to minimize risks. The decision to proceed should be made in consultation with a multidisciplinary team, including pulmonologists, otolaryngologists, and anesthesiologists.
Careful post-operative management is crucial for successful recovery. This includes regular monitoring of respiratory function, pain management, and prophylactic antibiotics to prevent infection. Patients may require temporary tracheostomy support to ensure adequate airway patency. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to assess healing progress and address any complications that might arise.

Exploring Minimally Invasive Options
Dilatation techniques, using balloon catheters or other specialized instruments to widen the narrowed tracheal segment, offer a less invasive alternative to tracheal shave. These procedures are often performed bronchoscopically, minimizing the need for extensive surgery. Balloon dilatation involves inflating a balloon catheter within the stenotic area to stretch and expand the tracheal lumen. This can be repeated multiple times depending on the response.
Stent placement, where a small, metal or plastic tube is inserted into the trachea to keep the airway open, represents another minimally invasive option. Stents provide structural support, preventing the trachea from collapsing and maintaining airway patency. Stents can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying condition and the patient’s response to treatment. The choice between balloon dilatation and stent placement depends on factors such as the location, severity, and cause of the stenosis.
Laser therapy can be used to precisely ablate excess tissue within the trachea, offering a minimally invasive approach to managing tracheal stenosis. This technique allows for targeted tissue removal with minimal collateral damage, potentially reducing complications compared to traditional tracheal shave. Laser therapy is often combined with other minimally invasive techniques for optimal results.
Careful selection of the minimally invasive option is crucial, guided by the specific characteristics of the stenosis, the patient’s overall health, and the expertise of the treating physician. The success rate of these procedures can be affected by factors such as the extent and location of the stenosis, the presence of underlying inflammation, and the patient’s compliance with post-procedural care.
Voice Restoration Techniques & Therapies
Vocal cord paralysis, a potential complication of tracheal shave, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Voice therapy, involving exercises and techniques to improve vocal cord function and strengthen the voice, plays a crucial role in managing this complication. A speech-language pathologist can provide personalized training programs to help patients regain their voice.
In cases of severe vocal cord paralysis, surgical interventions may be necessary. These include procedures such as medialization thyroplasty, which involves repositioning the vocal cords to improve their approximation during phonation. Injection laryngoplasty, where substances like collagen or fat are injected into the vocal cords, can also improve voice quality. The choice of surgical intervention depends on the severity and cause of the paralysis.
Technological advancements have led to the development of sophisticated voice prostheses, which can be implanted to assist in voice production. These devices provide an alternative pathway for air to pass over the vocal cords, facilitating speech. The suitability of a voice prosthesis is determined by the individual patient’s needs and clinical condition.
Regular monitoring and evaluation of voice function are essential to track progress and adjust treatment strategies as needed. A multidisciplinary approach, involving otolaryngologists, speech-language pathologists, and other healthcare professionals, is crucial for optimal voice restoration outcomes. The goal is to improve vocal quality, reduce voice fatigue, and enhance overall communication abilities.
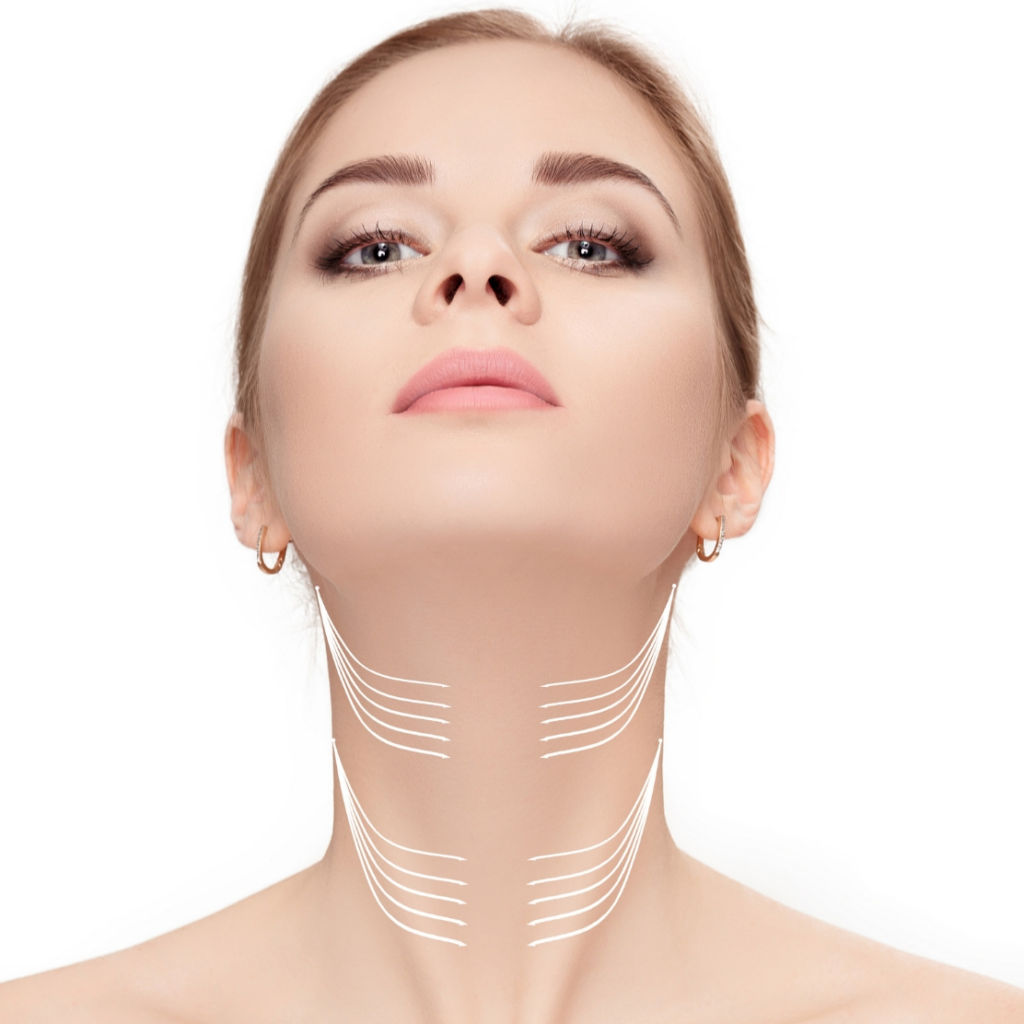

Advanced Surgical Alternatives & Outlook
Tracheal reconstruction, a more complex surgical procedure, may be considered in cases of severe or extensive tracheal stenosis where less invasive options have failed. This involves replacing the damaged or narrowed section of the trachea with a graft, often using a segment of the patient’s own tissue or a synthetic material. This requires a more extensive surgical approach and carries a higher risk of complications.
Tracheostomy, the surgical creation of an opening in the trachea to facilitate breathing, is sometimes necessary in cases of severe tracheal stenosis. While not a direct alternative to tracheal shave, it can provide a life-saving airway management strategy in critical situations. Tracheostomy allows for effective ventilation and can be temporary or permanent, depending on the individual’s clinical needs.
Ongoing research is focused on developing novel materials and techniques for tracheal reconstruction and stent design. Bioengineered tissues and scaffolds are being explored to create more biocompatible and durable replacements for damaged tracheal segments. These advancements promise to improve outcomes and reduce complications associated with tracheal surgery.
The future of tracheal stenosis management is likely to involve a personalized approach, integrating minimally invasive techniques, advanced surgical options, and supportive therapies to tailor treatment to individual patient needs and preferences. Continued research and technological advancements will play a vital role in improving the safety and efficacy of tracheal stenosis management and reducing the reliance on invasive procedures like tracheal shave.
While tracheal shave remains a viable option for treating tracheal stenosis, the availability of less invasive alternatives and advanced surgical techniques offers patients a broader range of treatment choices. The selection of the optimal approach requires careful consideration of individual factors, including the severity and location of the stenosis, the presence of co-morbidities, and patient preferences. A multidisciplinary team approach is crucial for successful management of tracheal stenosis, aiming for optimal airway patency and improved quality of life.
Visit Dr.MFO Instagram profile to see real patient transformations! Get a glimpse of the incredible results achieved through facial feminization surgery and other procedures. The profile showcases before-and-after photos that highlight Dr. MFO’s expertise and artistic vision in creating natural-looking, beautiful outcomes.
Ready to take the next step in your journey? Schedule a free consultation with Dr. MFO ( Best Facial Feminization Surgeon for You) today. During the consultation, you can discuss your goals, ask any questions you may have, and learn more about how Dr. MFO can help you achieve your desired look. Don’t hesitate to take advantage of this free opportunity to explore your options and see if Dr. MFO is the right fit for you.